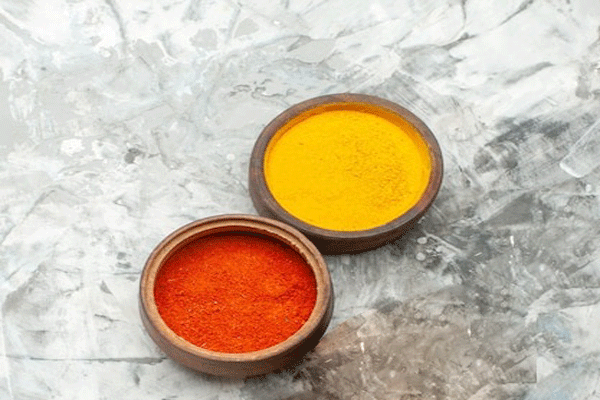
are turmeric and saffron the same thing?
saffron is a precious spice with a great scent and coloring power that’s known and loved by everyone all over the world. In addition to being used in cuisine, saffron is known as a precious component due to its medicinal parcels. Turmeric is also extensively used as a coloring spice in food and food assiduity. But these two substances, while being extensively used in cuisine, have medicinal parcels and different characteristics, so in this article, we’re going to compare these two spices.
How do saffron and turmeric differ?
Saffron is composed totally of the stamens from crocus flowers local to Crete at the same time as turmeric is an Indian rhizome associated with ginger. Saffron carries a yellow pigment however extra importantly, the stamens have a mild taste this is exclusive from the taste of turmeric. Saffron’s taste is subtly metal with earthy and nutty notes. Turmeric’s taste is barely peppery with a slightly sour note.
Saffron prices load extra than turmeric. It is taken into consideration as the world’s maximum luxurious spice specifically because of the quantity of labor and time it takes to reap the stamens. In order to get simply one pound of the spice, you want over 75,000 crocus blossoms. the crocus from which saffron comes is notoriously hard to grow. Turmeric is exceedingly clean to reap because it includes a dried floor root that appears loads like ginger and that grows effortlessly in tropical climates.
The spices differ in terms of some health benefits with saffron being considered an antidepressant and a memory booster. Turmeric is famend for its anti-inflammatory results and its capability withinside the remedy and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease.
The difference between turmeric and saffron
Saffron – a spice – is received from the saffron or Crocus Sativus flower. On the opposite hand, turmeric is likewise a spice, however, it comes from a plant known as Curcuma longa. It comes from the ginger family and grows in Southeast Asia or Asia.
The taste of turmeric with saffron:
Turmeric has an earthy and buttery taste while saffron has a milder taste compared to turmeric.
Cost:
The price of saffron is the most expensive spice in the world. Turmeric is more affordable than saffron and costs less.
Compositions and properties of saffron
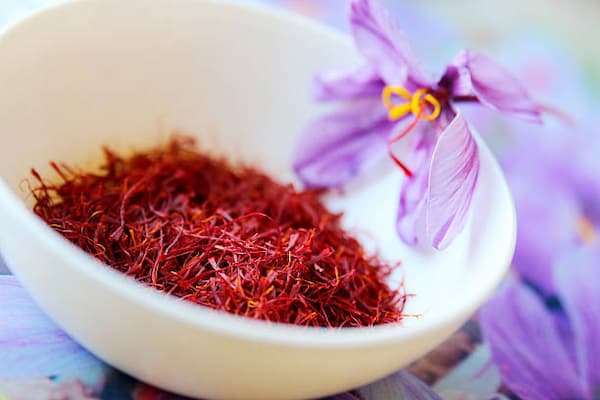
The specific composition of Mashhad saffron has outstanding in this plant. The primary part of saffron is the stigma of saffron, which offers color, flavor, and aroma to all forms of food. The results of laboratory research have shown that various chemical compounds of saffron flower stigma include carbohydrates, mucilage, minerals, and vitamins, especially riboflavin and thiamine. The coloring agent is crocin, carotene, lycopene, zeaxanthin, and anthocyanin, and the perfume agent is safranal and picrosin. This material has a few unstable oils and unique essences that deliver saffron a scent. And in general, it can be said that saffron contains the following main ingredients:
Crocin – has a coloring agent
Picrosin – has flavoring power
Safranal – has fragrance power
In addition, to be suitable for eating uses, the medicinal properties of saffron have constantly been considered. One of the maximum vital properties of saffron is to enhance the temper and wholesome functioning of the nerves. The nutrients in saffron assist the nervous system and decrease the incidence of sicknesses as a result of bad functioning of the nervous system. It is likewise advocated to apply saffron to enhance blood movement and hematopoiesis withinside the body. Saffron intake may be very appropriate for fixing sexual troubles and decreasing the signs of premenstrual syndrome and menstrual spasms. To examine extra approximately the benefit of saffron, refer to advice from the thing article Properties of saffron.
The taste and appearance of saffron
The color of saffron is different from turmeric. It has a distinctive crimson-red color and a taste similar to honey and flowers. If used a lot in cooking, it can cause bitterness or medicinal effects. Saffron is also used to flavor food.
Read more: sargol saffron | super negin saffron | saffron powder
Turmeric compounds and properties
Turmeric has sturdy antioxidant properties, that are used as a remedy to deal with many illnesses and is amply and effortlessly determined withinside the market. According to laboratory analysis, one tablespoon of turmeric powder contains 29 calories, 0. ninety grams of protein, 0.31 grams of fat, 6.31 grams of fiber, and 0. three grams of sugar. Turmeric can offer the each-day requirement of manganese, iron, potassium, and nutrition C.
The maximum vital compound in turmeric is known as curcumin, which offers medicinal properties. This substance has given turmeric remarkable anti-inflammatory residences and brought it a famous antioxidant. However, the quantity of curcumin in the amount of weight is handiest 3% of turmeric. To enjoy the anti-inflammatory residences of turmeric, human beings ought to eat multiple grams of it daily. And unfortunately, it’s far very tough to apply this quantity of turmeric in meal preparation. Therefore, to reveal the useful results of this substance, it’s far advocated to apply a complement containing an appropriate percentage of curcumin.
Another problem that curcumin has is that it isn’t always properly absorbed withinside the bloodstream and they want an auxiliary substance along with black pepper to facilitate its absorption. Supplements containing piperine – the equal substance discovered in black pepper – considerably grow the performance and effectiveness of curcumin.
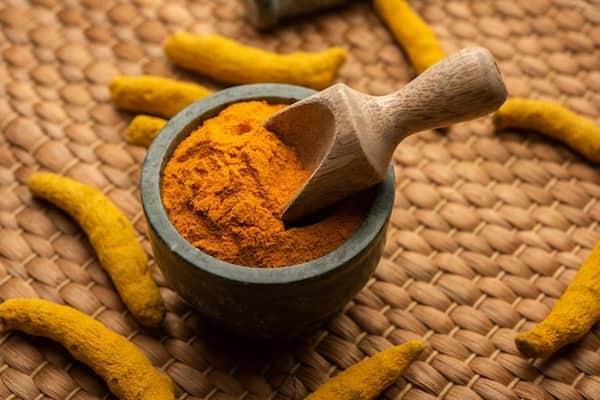
The flavor and appearance of turmeric
Turmeric is a member of the same family as ginger root. It is most commonly used in curry dishes because of its distinctive deep golden color. Turmeric can be used as a coloring agent due to its unique color.
Physical Differences Between Saffron and Turmeric
Saffron and turmeric are visually distinct. Saffron consists of delicate, deep red threads derived from the stigma of the Crocus sativus flower. These threads are thin, slightly curled, and have a rich crimson color with hints of orange. In contrast, turmeric is a bright yellow-orange rhizome, resembling ginger in shape. It is commonly found in its dried and ground form as a fine golden-yellow powder, making it easy to distinguish from saffron’s thread-like appearance.
Another key visual difference is how they dissolve in liquids. When steeped in water or milk, saffron gradually releases a rich golden-orange hue, while turmeric immediately disperses, turning the liquid a vibrant yellow. Additionally, saffron is significantly more expensive, and its threads are often sold in small quantities, whereas turmeric is widely available in bulk and used generously in cooking.
Chemical Composition and Nutritional Value of Saffron and Turmeric
Saffron and turmeric have distinct chemical compositions that contribute to their unique properties. Saffron contains crocin, picrocrocin, and safranal, which are responsible for its color, mild bitterness, and distinctive aroma. It is rich in antioxidants, including carotenoids, which contribute to its potential health benefits. Although used in small amounts, saffron provides essential minerals like manganese, iron, and potassium.
Turmeric, on the other hand, owes its vibrant yellow color to curcumin, a powerful compound with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Unlike saffron, turmeric is often consumed in larger quantities, providing notable amounts of fiber, vitamin C, and iron. While both spices offer health benefits, turmeric is more commonly studied for its medicinal properties, particularly in relation to reducing inflammation and supporting joint health.
Flavor and Aroma Comparison: Saffron vs. Turmeric
Saffron has a complex and delicate flavor profile with floral, honey-like, and slightly earthy undertones. Its aroma is subtly sweet and grassy, often described as warm and luxurious. When infused in dishes, saffron imparts a rich, slightly bitter taste with a lingering sweetness, making it a prized ingredient in gourmet cuisines like Persian, Indian, and Mediterranean dishes.
Turmeric, on the other hand, has a much stronger, earthier flavor with a slightly bitter and peppery taste. It lacks the floral sweetness of saffron and instead offers a more robust, musky aroma with hints of ginger and mustard. Unlike saffron, which is used in small amounts primarily for its aroma and color, turmeric is often added in larger quantities to curries, soups, and stews for both its taste and health benefits.
Culinary Uses of Saffron and Turmeric
Saffron is a highly prized spice in culinary traditions worldwide, especially in Middle Eastern, Mediterranean, and Indian cuisines. Its delicate floral aroma and distinct golden-orange hue make it an essential ingredient in dishes such as Persian saffron rice, Spanish paella, and Indian biryanis. Saffron is often steeped in warm water or milk before being added to dishes, allowing its color and flavor to infuse fully. It is also used in desserts like saffron-infused ice cream, cakes, and puddings, enhancing both taste and presentation.
Turmeric, in contrast, is a staple in many Asian and Middle Eastern cuisines, widely used in savory dishes for its earthy, slightly bitter flavor. It is a key ingredient in curry powders, spice blends, and stews, providing a warm, golden color to foods like Indian curries, lentil soups, and stir-fries. Turmeric is also used in beverages such as golden milk and herbal teas, valued not only for its taste but also for its health benefits. Unlike saffron, turmeric is more versatile in terms of quantity, as it can be used generously without overpowering a dish.
Medicinal Benefits and Healing Effects of Saffron and Turmeric
Saffron has long been recognized for its medicinal properties, particularly for its ability to enhance mood and mental well-being. Studies suggest that saffron may help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety due to its bioactive compounds, such as crocin and safranal. Additionally, saffron contains powerful antioxidants that contribute to overall cellular health, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. It is also known to support eye health and improve memory function.
Turmeric, on the other hand, is widely studied for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, primarily due to its active compound, curcumin. Turmeric has been shown to help reduce chronic inflammation, making it beneficial for conditions such as arthritis and joint pain. It also plays a role in improving digestion, supporting liver health, and boosting the immune system. Unlike saffron, which is often consumed in small doses, turmeric is commonly taken as a supplement or consumed in larger amounts to maximize its health benefits.
Comparison of Saffron and Turmeric’s Effects on Skin Health
Saffron is highly valued in skincare for its brightening and anti-aging properties. Rich in antioxidants, it helps protect the skin from environmental damage and oxidative stress, which contribute to premature aging. Saffron’s natural antibacterial properties make it effective in treating acne and reducing skin inflammation. It is often used in face masks, serums, and creams to promote a radiant complexion, reduce pigmentation, and even out skin tone.
Turmeric, in contrast, is well known for its powerful anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects on the skin. It is widely used in traditional remedies to treat acne, eczema, and other skin conditions. The curcumin in turmeric helps reduce redness, swelling, and irritation, making it ideal for soothing sensitive skin. Turmeric-based masks and creams are popular for their ability to reduce dark spots and improve overall skin texture. While both saffron and turmeric contribute to healthier skin, turmeric is more commonly used for treating inflammatory skin conditions, whereas saffron is favored for its brightening and rejuvenating effects.
Differences Between Saffron and Turmeric in Traditional and Modern Medicine
In traditional medicine, saffron has been highly valued for its mood-enhancing, digestive, and aphrodisiac properties. Ancient Persian, Indian, and Chinese medicine used saffron to treat depression, anxiety, and digestive disorders. It was also believed to improve circulation and support heart health. Saffron-infused teas and tonics were commonly used for their calming effects and to relieve menstrual discomfort. Traditional practitioners often prescribed saffron in small doses due to its potency and high value.
Turmeric, on the other hand, has been a cornerstone of Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine for centuries. It has been widely used as a natural anti-inflammatory remedy to treat joint pain, respiratory conditions, and digestive issues. In traditional healing practices, turmeric paste was applied to wounds and infections due to its antimicrobial properties. Modern medicine has expanded on these traditional uses, with scientific studies supporting turmeric’s role in reducing chronic inflammation, improving gut health, and even potentially preventing certain cancers. Unlike saffron, turmeric is often consumed in larger quantities and is a common ingredient in herbal supplements and health drinks.
Price and Availability: Why Is Saffron More Expensive Than Turmeric?
Saffron is one of the most expensive spices in the world due to the labor-intensive process required for its cultivation and harvesting. Each saffron flower (Crocus sativus) produces only three delicate red stigmas, which must be handpicked and carefully dried. It takes approximately 75,000 to 100,000 flowers to produce just one kilogram of saffron, making its production highly labor-intensive and time-consuming. Additionally, saffron grows in limited regions with specific climate conditions, further contributing to its high price.
Turmeric, in contrast, is much more affordable and widely available. It is derived from the rhizome of the Curcuma longa plant, which grows abundantly in tropical regions such as India, China, and Southeast Asia. Unlike saffron, turmeric is harvested in bulk, processed mechanically, and easily ground into powder. Its high yield, lower labor costs, and widespread cultivation make turmeric significantly more accessible and inexpensive compared to saffron. This affordability allows turmeric to be used generously in cooking, supplements, and skincare products.
Methods to Identify Authentic Saffron and Turmeric
To determine if saffron is genuine, there are several tests that can be performed. Real saffron threads are deep red with slight orange tips, and they do not break easily when rubbed between the fingers. When placed in warm water or milk, authentic saffron gradually releases a rich golden hue over several minutes without instantly dissolving. A strong, floral, and slightly honey-like aroma is another indicator of purity. Additionally, genuine saffron will not leave an artificial residue or color the water unnaturally fast, unlike fake saffron that may be dyed.
Turmeric authenticity can be tested by checking its color, texture, and solubility. Pure turmeric powder has a deep yellow-orange color and a distinct earthy aroma. To test for adulteration, a small amount of turmeric can be mixed with water; if artificial coloring is present, it will leave a bright streak or settle at the bottom. Another method is the iodine test: adding a few drops of iodine to turmeric powder—if it turns dark blue, it may be mixed with starch or artificial fillers. Buying turmeric in whole rhizome form and grinding it at home is one of the best ways to ensure purity.
Comparison of Saffron and Turmeric’s Effects on Mood and Depression
Saffron has been extensively studied for its potential antidepressant and mood-enhancing properties. The bioactive compounds crocin, safranal, and picrocrocin are believed to influence neurotransmitter activity, particularly by increasing serotonin levels in the brain. Research suggests that saffron supplementation may be as effective as some conventional antidepressants, such as fluoxetine, in alleviating mild to moderate depression. Additionally, saffron’s antioxidant properties help reduce oxidative stress, which is often linked to mental health disorders.
Turmeric, specifically its active compound curcumin, has also been shown to have mood-boosting effects. Curcumin has neuroprotective properties and can enhance levels of serotonin and dopamine, which play crucial roles in regulating mood. Studies indicate that curcumin supplementation may help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, particularly when combined with black pepper (piperine) to enhance absorption. While both saffron and turmeric have antidepressant potential, saffron is often considered more potent in mood regulation, whereas turmeric provides additional anti-inflammatory benefits that support overall brain health.
Cultivation and Production: Saffron vs. Turmeric
Saffron cultivation is a highly labor-intensive process that requires specific climatic conditions. It is primarily grown in regions with dry, warm summers and cold winters, such as Iran, India (Kashmir), and Spain. Saffron comes from the Crocus sativus flower, which blooms for only a few weeks each year. Each flower produces just three red stigmas, which must be hand-harvested with great care. After collection, the stigmas are carefully dried to preserve their aroma and potency. Due to this meticulous harvesting process, saffron production is both time-consuming and expensive.
Turmeric, on the other hand, is cultivated in tropical and subtropical regions, including India, China, Indonesia, and Thailand. It is derived from the rhizome of the Curcuma longa plant, which grows underground like ginger. Unlike saffron, turmeric can be harvested in bulk using mechanical methods. After harvesting, the rhizomes are boiled, dried, and ground into a fine powder. Because of its ease of cultivation and high yield, turmeric is produced on a much larger scale and is significantly more affordable than saffron.
Differences in Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of Saffron and Turmeric
Saffron contains powerful antioxidants, such as crocin, safranal, and kaempferol, which help protect cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. While saffron is not traditionally known as a primary anti-inflammatory agent, its compounds have been shown to reduce markers of chronic inflammation in conditions like metabolic syndrome and neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, saffron’s antioxidants contribute to improved brain health, cardiovascular protection, and immune system support.
Turmeric, however, is widely recognized as one of the most potent natural anti-inflammatory agents due to its high curcumin content. Curcumin inhibits inflammatory pathways in the body, making it beneficial for managing arthritis, autoimmune diseases, and chronic pain conditions. Additionally, turmeric’s strong antioxidant properties help neutralize free radicals and prevent cellular damage. While both saffron and turmeric have health benefits, turmeric is superior for reducing inflammation, whereas saffron is more effective in neuroprotection and mood enhancement.
Role of Turmeric and Saffron in Boosting the Immune System
Saffron is rich in antioxidants such as crocin, safranal, and kaempferol, which help protect immune cells from oxidative stress. These compounds contribute to reducing inflammation and strengthening the body’s defense mechanisms against infections. Additionally, saffron has been studied for its potential to enhance white blood cell activity, which plays a crucial role in fighting off pathogens. Regular consumption of saffron in moderate amounts may help improve immune resilience and overall well-being.
Turmeric, on the other hand, is widely recognized for its potent immune-boosting properties due to its high curcumin content. Curcumin has strong anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antiviral effects, making it beneficial in preventing and managing infections. Studies suggest that turmeric can help regulate immune responses and support gut health, which is closely linked to immune function. Unlike saffron, turmeric is often consumed in larger quantities, making it a more accessible and practical choice for enhancing immunity through diet and supplementation.
Applications of Turmeric and Saffron in the Cosmetic and Skincare Industry
Saffron has long been used in skincare for its brightening and anti-aging properties. Its antioxidants help protect the skin from environmental damage and premature aging. Saffron is often found in high-end creams, serums, and face masks that aim to improve skin tone, reduce pigmentation, and promote a radiant complexion. Additionally, its antibacterial properties make it effective in treating acne and soothing inflammation. In traditional beauty treatments, saffron-infused oils and pastes have been used to enhance skin glow and texture.
Turmeric is equally popular in the beauty industry, primarily for its powerful anti-inflammatory and healing properties. It is widely used in skincare products designed to treat acne, eczema, and hyperpigmentation. Turmeric-based face masks and creams help reduce redness, soothe irritation, and even out skin tone. Additionally, its antibacterial properties make it effective in preventing breakouts. Unlike saffron, which is mostly used for brightening and rejuvenation, turmeric is favored for treating skin conditions and improving overall skin health.
Comparison of Color Effects and Impact in Foods and Beverages
Saffron is prized for its rich golden-orange hue, which adds a luxurious touch to dishes and drinks. When steeped in water, milk, or broth, saffron gradually releases its deep color, enhancing both visual appeal and flavor. It is commonly used in rice dishes like Persian saffron rice and Spanish paella, as well as in desserts and beverages such as saffron-infused teas and milk. Due to its strong pigment, even a small amount of saffron can dramatically enhance the color and presentation of food.
Turmeric, in contrast, produces a vibrant yellow color and is widely used as a natural food dye. Unlike saffron, turmeric’s color is more intense and spreads instantly when added to liquids or food. It is a key ingredient in curries, soups, and golden milk, providing both color and a distinctive earthy flavor. While saffron’s color is more subtle and warm-toned, turmeric gives a bold yellow shade, making it a preferred choice for mass food production and dyeing purposes.
FAQ: The Differences Between Turmeric and Saffron
1. What is the main difference between turmeric and saffron?
Turmeric comes from the rhizome of the Curcuma longa plant, while saffron is derived from the stigmas of the Crocus sativus flower.
2. Why is saffron more expensive than turmeric?
Saffron is costly due to its labor-intensive harvesting process, as each flower produces only three delicate stigmas. In contrast, turmeric is grown in bulk and processed easily.
3. How do turmeric and saffron differ in flavor?
Turmeric has an earthy, slightly bitter taste, while saffron has a floral, slightly sweet, and honey-like flavor.
4. Which spice is better for health benefits?
Both are beneficial; turmeric is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, while saffron is valued for its mood-enhancing and neuroprotective effects.
5. How do they impact food color?
Turmeric gives food a bold yellow hue, while saffron imparts a golden-orange color.
5. Can I use saffron instead of turmeric?
Saffron is completely different from turmeric. Saffron has a wonderful taste and aroma, at the same time it has a nectar-like taste in food. Saffron gives a unique aroma to food, but turmeric does not have this aroma at all. Saffron also has properties that no spice has.
Buy Premium Saffron from Tida Silk Road Trading
Experience the finest premium saffron with Tida Silk Road Trading! Sourced from the best farms, our saffron is 100% pure, aromatic, and rich in color—perfect for cooking, health, and beauty.
Why choose us?
✔ Highest Quality – Handpicked, fresh, and naturally dried
✔ Vibrant Color & Aroma – Enhances your dishes beautifully
✔ Competitive Prices – Premium saffron at the best value
✔ Worldwide Shipping – Delivered fresh to your doorstep
Add a touch of luxury to your meals with Tida Silk Road Trading Saffron! 🌿
📩 Order Now! Contact us for wholesale and retail prices.
- website → buy high-quality dried fruit products